World's first recipient to receive a pig heart tragically dies
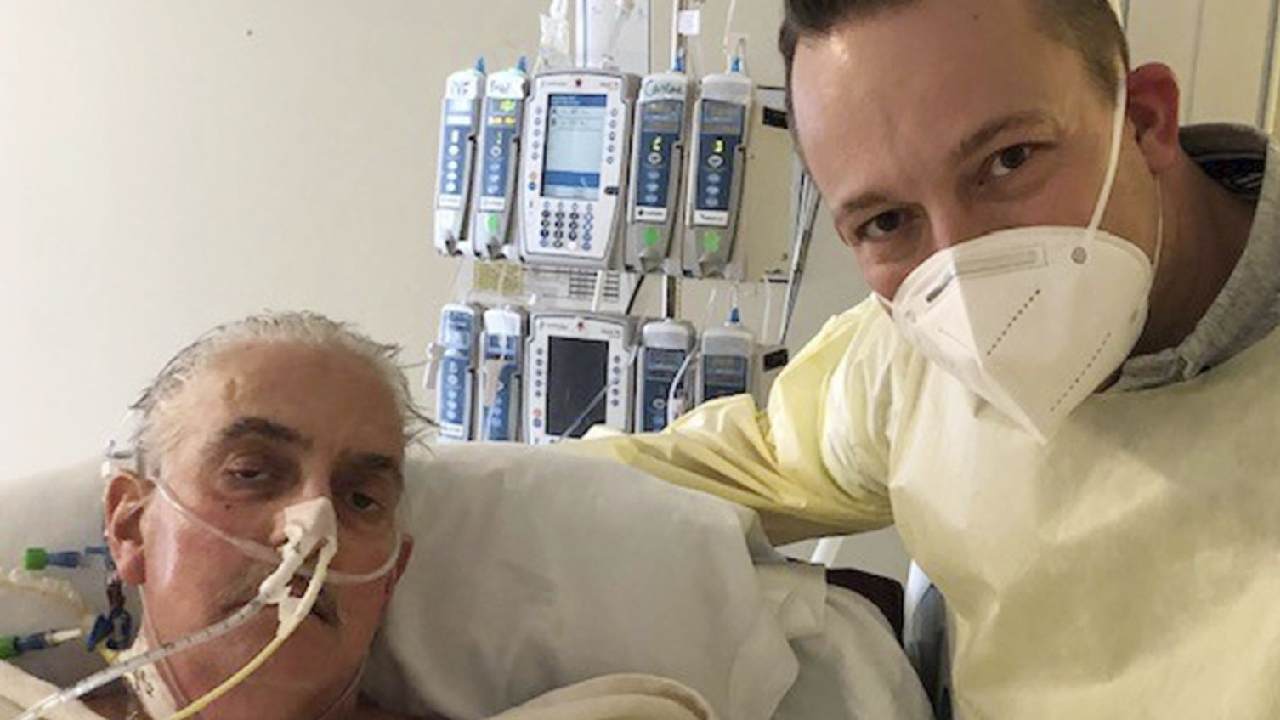
The first person to receive a heart transplant from a pig has died, two months after the groundbreaking experiment.
David Bennett, aged 57, died Tuesday at the University of Maryland Medical Centre. Doctors didn't give an exact cause of death, saying only that his condition had begun deteriorating several days earlier.
Bennett's son praised the hospital for offering the last-ditch experiment, saying the family hoped it would help further efforts to end the organ shortage.
"We are grateful for every innovative moment, every crazy dream, every sleepless night that went into this historic effort," David Bennett Jr. said in a statement released by the University of Maryland School of Medicine. "We hope this story can be the beginning of hope and not the end."
Doctors for decades have sought to one day use animal organs for life-saving transplants. Bennett, a handyman from Hagerstown, Maryland, was a candidate for this newest attempt only because he otherwise faced certain death, ineligible for a human heart transplant, bedridden and on life support, and out of other options.
After the operation on the 7th of January, Bennett's son told the Associated Press his father knew there was no guarantee it would work.
Prior attempts at such transplants - or xenotransplantation - have failed largely because patients' bodies rapidly rejected the animal organ. This time, the Maryland surgeons used a heart from a gene-edited pig. Scientists had modified the animal to remove pig genes that trigger the hyper-fast rejection and add human genes to help the body accept the organ.
"We are devastated by the loss of Mr Bennett. He proved to be a brave and noble patient who fought all the way to the end," Dr Bartley Griffith, who performed the surgery at the Baltimore hospital, said in a statement.
Other transplant experts praised the Maryland team's landmark research and said Bennett's death shouldn't slow the push to figure out how to use animal organs to save human lives.
"It was an incredible feat that he was kept alive for two months and was able to enjoy his family," Montgomery added.
The Food and Drug Administration had allowed the dramatic experiment under "compassionate use" rules for emergency situations. Bennett's doctors said he had heart failure and an irregular heartbeat, plus a history of not complying with medical instructions. He was deemed ineligible for a human heart transplant that requires strict use of immune-suppressing medicines, or the remaining alternative, an implanted heart pump.
From Bennett's experience, "we have gained invaluable insights learning that the genetically modified pig heart can function well within the human body while the immune system is adequately suppressed", said Dr Muhammad Mohiuddin, scientific director of the Maryland university's animal-to-human transplant program.
Patients may see Bennett's death as suggesting a short life-expectancy from xenotransplantation, but the experience of one ill person cannot predict how well this procedure ultimately will work, said ethics expert Karen Maschke of The Hastings Center.
Transplant centres need to start educating their patients now about what to expect as this science unfolds, said Maschke, who with funding from the National Institutes of Health is developing ethics and policy recommendations on who should be allowed in the first studies of pig kidneys and what they need to know before volunteering.
Image: University of Merryland
